Objective: The aim of this study was to investigate ErbB2 expression in osteochondroma and its relationship with clinicopathologic features of osteochondroma, so as to identify a new biomarker for the malignant transformation potential of osteochondroma.
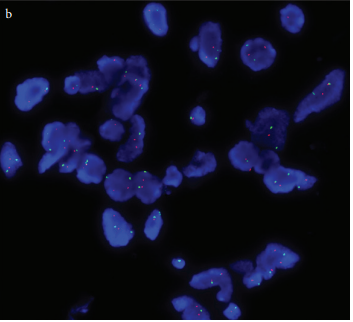
Methods: Immunohistochemistry (IHC) and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) were used to investigate the expression status of ErbB2 protein and gene in 30 osteochondroma tissues and 20 non-neoplastic bone tissues. The association of ErbB2 gene and protein expression with clinicopathological parameters of osteochondroma was analyzed by using the χ2 test and Fishers exact test.
Results: ErbB2 protein was found to be over-expressed in 4 of 30 (13.3%) osteochondromas and 1 of 20 (5%) non-neoplastic bone samples, which were not statistically significant (p=0.336). However, 13 of the 30 (43.3%) osteochondromas showed ErbB2 gene amplification, which was failed to be observed in any of the non-neoplastic bone tissue. ErbB2 gene amplification in osteochondroma was significantly higher compared with that in non-neoplastic bone tissue (p=0.001). In addition, the ErbB2 gene amplification was closely associated with clinical pathological parameters of osteochondroma, including high expression of cellularity (p=0.001), presence of binucleated cells (p=0.001), nuclear pleomorphism (p=0.003), calcification (p=0.002), nodularity (p=0.002), necrosis (p=0.009) and cartilage thickness (p=0.026). The association of the gene amplification with other clinicopathological parameters of osteochondroma, including permeation of trabecular bone, cystic/mucoid changes, mitosis, radiographic appearance, cap volume and subtype of osteochondroma was not observed. The over-expression of ErbB2 protein was not found to be associated with the above stated clinical pathological parameters of osteochondroma.
Conclusion: ErbB2 gene amplification was associated with adverse clinicopathological status of osteochondroma and could serve as an index for malignant conversion of osteochondroma. Further research is required to verify the predictive values of ErbB2 for osteochondroma.
Level of Evidence: Level IV, Diagnostic Study
Cite this article as: Huang Z, Wang SL, Huang QD, Li WD, Chen H, Lin JH. Clinicopathological value of ErbB2 gene and protein expression in osteochondroma. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc 2020; 54(1): 34-41.



.png)
.png)